Sometimes people confuse vibration welding and ultrasonic welding because both processes use vibration energy to weld plastic components. However, these two processes are very different from each other. Let's look at the differences between these two processes and how to use them to your advantage.
Vibration welding plastic
Both vibration welding and ultrasonic welding use vibration to generate friction and heat to weld plastics.
Vibration direction
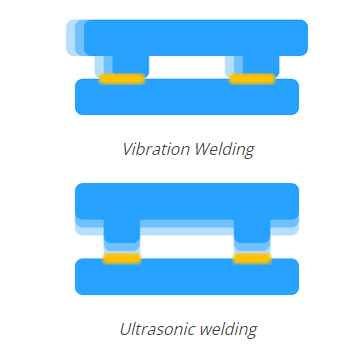
The vibration welding process vibrates one part relative to the other part in a linear left-to-right motion. Take a moment to rub your hands, like trying to get warm from the cold. The action you make is the same as the action made by the vibration welder on the two parts. The friction between two objects generates heat for welding.
In contrast, the ultrasonic welding process causes one component to vibrate perpendicular to the other, like a jackhammer on a sidewalk. Vibrating in this direction may seem counterintuitive, but ultrasonic welding vibrates very fast, which causes molecular friction and generates heat.
Vibration frequency
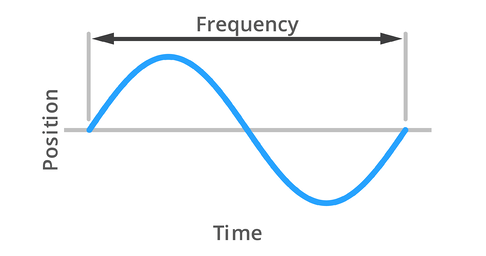
Frequency is a measure of how much vibration is completed in one second. The vibration welding process vibrates approximately 120-240 times per second, or 120-240 Hz, depending on the size of the part being welded. This frequency is completely within the range of human hearing, so the vibration equipment uses a soundproof enclosure to protect the machine operator from the deafening fog horn-like sound.
Ultrasonic welding vibrates at an ultrasonic frequency, which is where the name comes from. So, what is the ultrasonic frequency? They are higher than the human ear can hear, usually 20,000 Hz or 20 kHz. Most ultrasonic processes operate between 20 and 40 kHz. Some work at 15 kHz, which is not technically within the ultrasonic range, but is still considered as ultrasonic welding. The 20-40 kHz application is quieter than vibration, but due to the lower resonance frequency of plastic parts, it does produce some sharp, sharp sounds.
Vibration amplitude
Amplitude is the distance between the two furthest points of vibrational motion. In vibration welding, the amplitude in high-frequency machines is usually between 0.4 and 1.8 mm, while the amplitude in low-frequency machines is usually between 1.8 and 4.0 mm. The lower the amplitude, the higher the frequency.
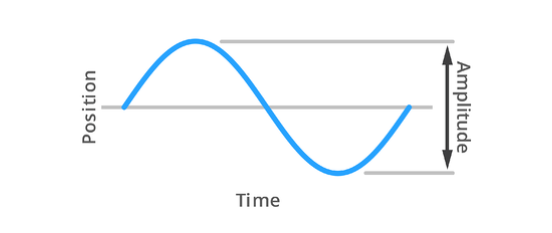
In contrast, the amplitude of ultrasonic welding is much smaller. Many applications use between 25 and 125 microns or 0.025-0.125 mm. Just like in vibration welding, the lower the amplitude, the higher the frequency.
Welding time
Vibration welding is a fairly fast process, with a typical cycle time in the range of 5-10 seconds, but ultrasonic welding is much faster, with a typical cycle time between 1 and 3 seconds.
Part size
Vibration can weld components of various sizes. It can be used to weld small components such as car armrests and glove boxes, as well as large components such as washing machine drums and car dashboards.
Ultrasound is limited to smaller welds. Some components may be very small, such as flash drives and earphones, and the largest component that can be ultrasonically welded is usually no more than 6 x 8 inches. However, it is common to see multiple ultrasonic tools or stacks being used to weld several small parts to a larger part, such as welding ports and brackets to the engine manifold.
Best application
All in all, vibration welding is a great process because it is faster than other processes that can weld large components such as hot plate welding and infrared welding. If the application requires it, it can produce strong, strong welds that are leak-proof. It is very suitable for the following applications:
-
Dash board
-
Intake manifold
-
Glove box
-
Armrest
-
Taillight
-
Electrical tools
-
Surgical Instruments
-
Filter
-
Household appliances
-
And more...
Ultrasonic welding is a universal process, very fast and very suitable for small parts. It can also produce leak-proof welds and is very useful when welding small parts to larger components. It is most suitable for the following applications:
-
Small electronic enclosure
-
Package
-
Ports and brackets are installed on larger parts such as intake manifolds
-
Dashboard trim
-
Car sound insulation pad
-
And more...





