
Ultrasonic Homogenizers
Ultrasonic homogenizers are powerful tools to mix and homogenize solid-liquid and liquid-liquid suspensions. Ultrasonic homogenization is a mechanical process to reduce particles in a liquid so that they become uniformly small and evenly distributed.
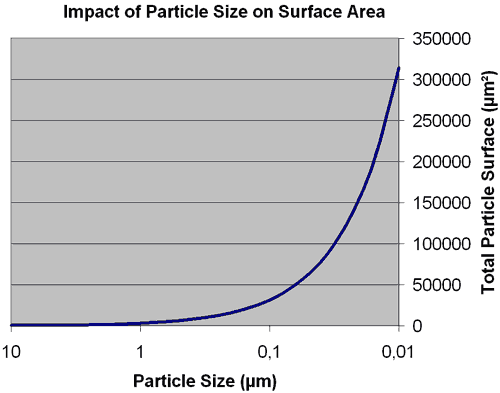
Impact of Ultrasonic Homogenizers
Ultrasonic homogenizers are very efficient for the reduction of soft and hard particles. The homogenization is based on cavitation. When liquids are exposed to intense ultrasonication, sound waves propagate through the liquid causing alternating high-pressure and low-pressure cycles (approx. 20000 cycles/sec.). During the low-pressure cycle, high-intensity small vacuum bubbles are created in the liquid, as the liquid vapor pressure is attained.

When the bubbles reach a certain size, they collapse violently during a high-pressure cycle. During this implosion very high pressures and high speed liquid jets are generated locally. The resulting currents and turbulences disrupt particle agglomerates and lead to violent collisions between individual particles.
© Copyright: 2026 Hangzhou Altrasonic Technology Co.,Ltd All Rights Reserved

IPv6 network supported
Scan to WhatsApp
